According to most benchmarks, the NVIDIA H100 is currently the top GPU for AI training and inference. While there are new contenders like the GB200 already on the horizon, the next big shift in GPU performance is just around the corner. The NVIDIA H200 will be available on premium cloud GPU platforms like DataCrunch before the end of 2024.
In this article we compare H200 and H100 GPU architectures, key features, benchmark results, and pricing considerations to help you choose the best GPU for your up-coming AI workloads.
What is the H200?
The NVIDIA H200 is a Tensor Core GPU specifically designed to be used in high performance computing and AI use-cases. It’s based on the Hopper GPU architecture, designed to achieve maximal performance in parallel computing.
NVIDIA introduced the H200 in November 2023 as a direct upgrade to the H100 that promises better performance, efficiency, and scalability. With 141 gigabytes (GB) of HBM3e memory at 4.8 terabytes per second (TB/s) it nearly doubles the capacity of the NVIDIA H100 in core AI workloads such as LLM inference.
Until new Blackwell-series GPUs are more widely available on the market, the H200 is likely to be the fastest and most cost-efficient GPU to use in most demanding AI workloads. It will also come with a significantly lower total cost of ownership (TCO) than the H100.
H200 vs H100 Specs Comparison
Technical Specifications | H100 SXM | H200 SXM |
|---|---|---|
Form Factor | SXM5 | SXM5 |
FP64 | 34 TFLOPS | 34 TFLOPS |
FP64 Tensor Core | 67 TFLOPS | 67 TFLOPS |
FP32 | 67 TFLOPS | 67 TFLOPS |
TF32 Tensor Core* | 989 TFLOPS | 989 TFLOPS |
BFLOAT16 Tensor Core* | 1,979 TFLOPS | 1,979 TFLOPS |
FP16 Tensor Core* | 1,979 TFLOPS | 1,979 TFLOPS |
FP8 Tensor Core* | 3,958 TFLOPS | 3,958 TFLOPS |
INT8 Tensor Core* | 3,958 TFLOPS | 3,958 TFLOPS |
GPU Memory | 80 GB | 141 GB |
GPU Memory Bandwidth | 3.35 TB/s | 4.8 TB/s |
Max Thermal Design Power (TDP) | Up to 700W (configurable) | Up to 700W (configurable) |
Multi-Instance GPUs | Up to 7 MIGs @10GB each | Up to 7 MIGs @16.5GB each |
Interconnect | - NVIDIA NVLink®: 900GB/s | PCIe Gen5: 128GB/s <br> NVIDIA NVLink®: 900GB/s <br>PCIe Gen5: 128GB/s |
The H200 is expected to be an upgraded version of the H100 retaining a similar range of computational capabilities (FP64 to INT8). Under the hood the H100 and H200 share many of the same components, networking configurations and architectural choices.
The key difference comes in the massive increase in VRAM, with 141GB of HBM3e memory offering a substantial upgrade to the H100’s 80GB HBM3.
The H200 is capable of 43% higher GPU memory bandwidth than the H100, with a peak of 4.8TB/s and 900GB/s of P2P bandwidth.
H200 vs H100 AI Workload Comparison
The larger and faster memory of the H200 will have a significant impact on core AI workloads. The H200 boosts inference speed by up to 2x compared to H100 GPUs on LLMs like Llama2 70B.
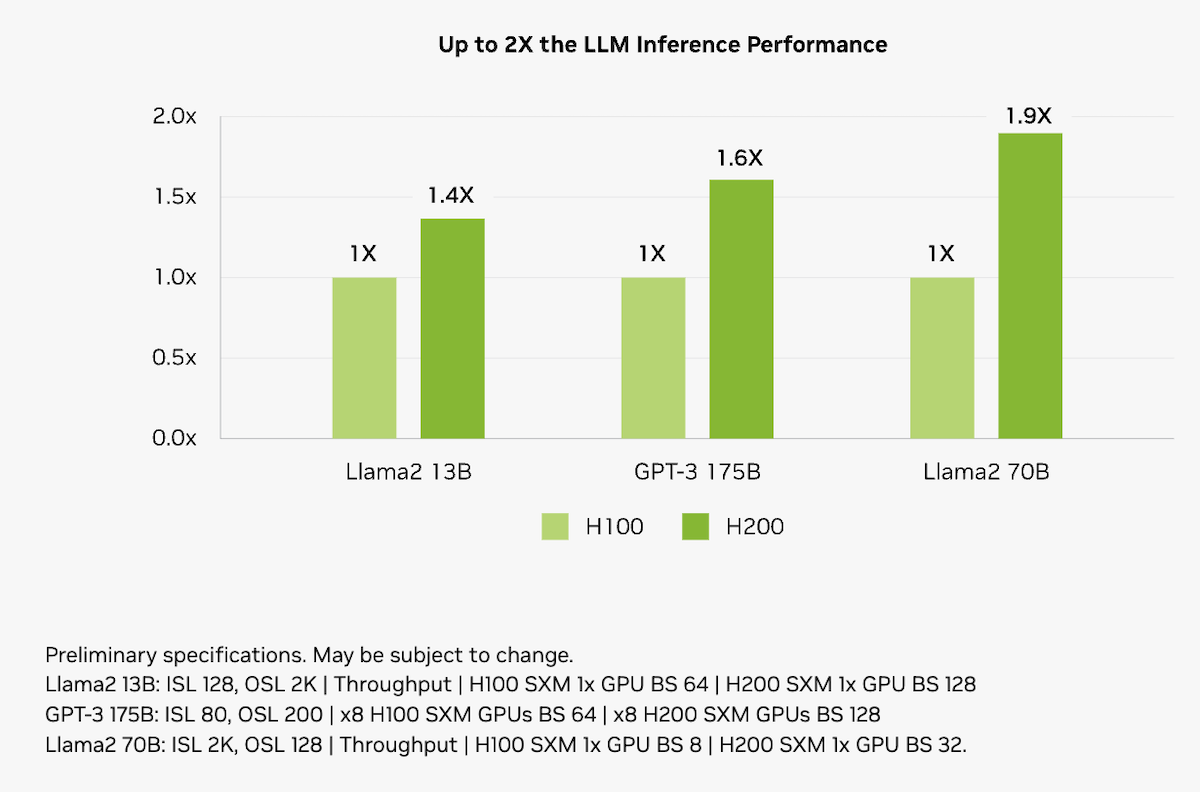
H200 vs H100 total cost of ownership (TCO) comparison. Source: nvidia.com
NVIDIA estimates that the energy use of the H200 will be up to 50% lower than the H100 for key LLM inference workloads, resulting in a 50% lower total cost of ownership over the lifetime of the device.
How H200 and H100 HGX Systems Compare
As the need for AI training increases with ever-larger language models, the computational limits move beyond a single GPU architecture. NVIDIA addresses this challenge with the HGX AI supercomputing platform.
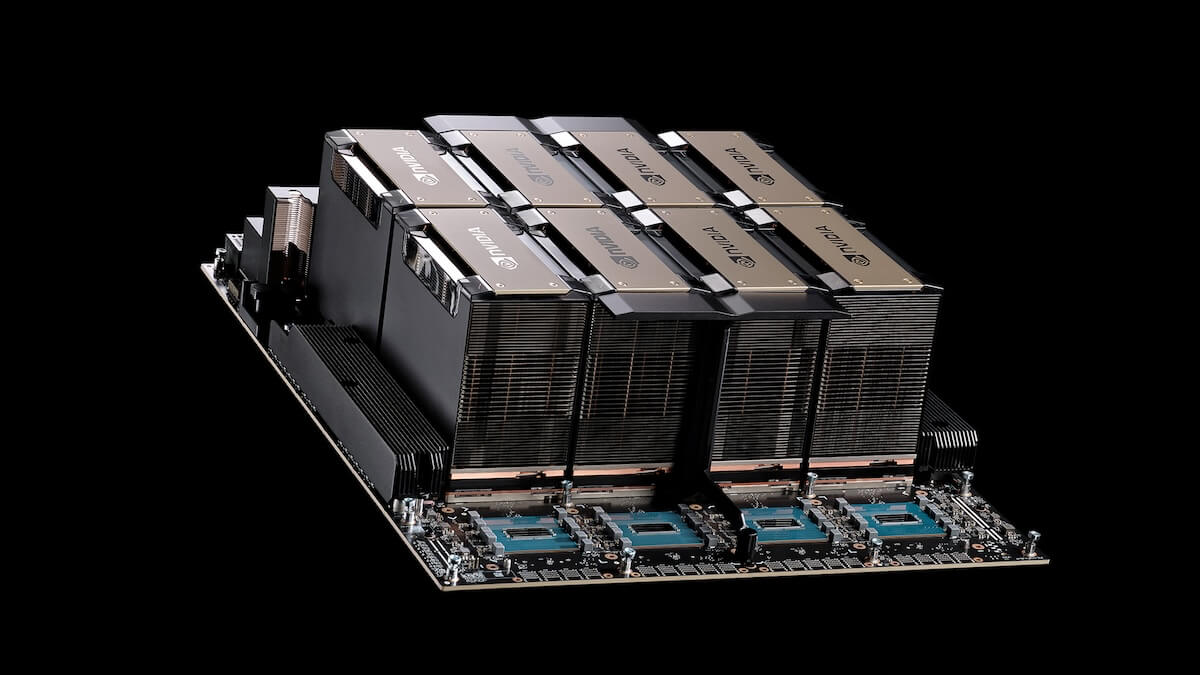

H200 HGX system with NVLink Switch chips. Source: nvidia.com
The HGX integrates up to 8 H200 GPUs with high-speed NVLink interconnects and optimized software stacks including CUDA, Magnum IO and Doca. HGX gives you a versatile platform that can scale from single systems to large datacenter clusters.
Comparison of HGX H100 and H200 8-GPU Systems
Feature | HGX H100 8-GPU | HGX H200 8-GPU |
|---|---|---|
FP8 TFLOPS | 32,000 | 32,000 |
FP16 TFLOPS | 16,000 | 16,000 |
GPU-to-GPU Bandwidth | 900GB/s | 900GB/s |
Quantum-2 | ||
InfiniBand networking | 400GB/s | 400GB/s |
Total Aggregate Bandwidth | 3.6TB/S | 7.2TB/s |
Memory | 640GB HBM | 1.1TB HBM3e |
NVLink | Fourth generation | Fourth generation |
GPU Aggregate Bandwidth | 27GB/s | 38GB/s |
Architecturally the H100 and H200 HGX systems share many of the same design choices, but the H200 sees a 2x increase in total aggregate bandwidth and a 72% increase in available total memory.
Cost of the H100 and H200
Neither the H100 nor H200 are GPUs you can purchase off the shelf. The cost of a single GPU or HGX system depends on your configuration and delivery options.
We can expect the H200 to cost approximately 20% more per hour when accessed as a virtual machine instance on cloud service providers.
Hourly cost for the H100 and the H200 on DataCrunch Cloud Platform:
H100 SXM5 | H200 SXM5 | |
|---|---|---|
On-demand price /h | $3.35 | $4.02 |
2-year contract /h | $2.51 | $3.62 |
Real-world implications
Over the past couple of years demand for NVIDIA’s datacenter GPUs like the H100 has far exceeded supply, leading to a scramble for limited computing resources between hyper-scalers and new AI startups.
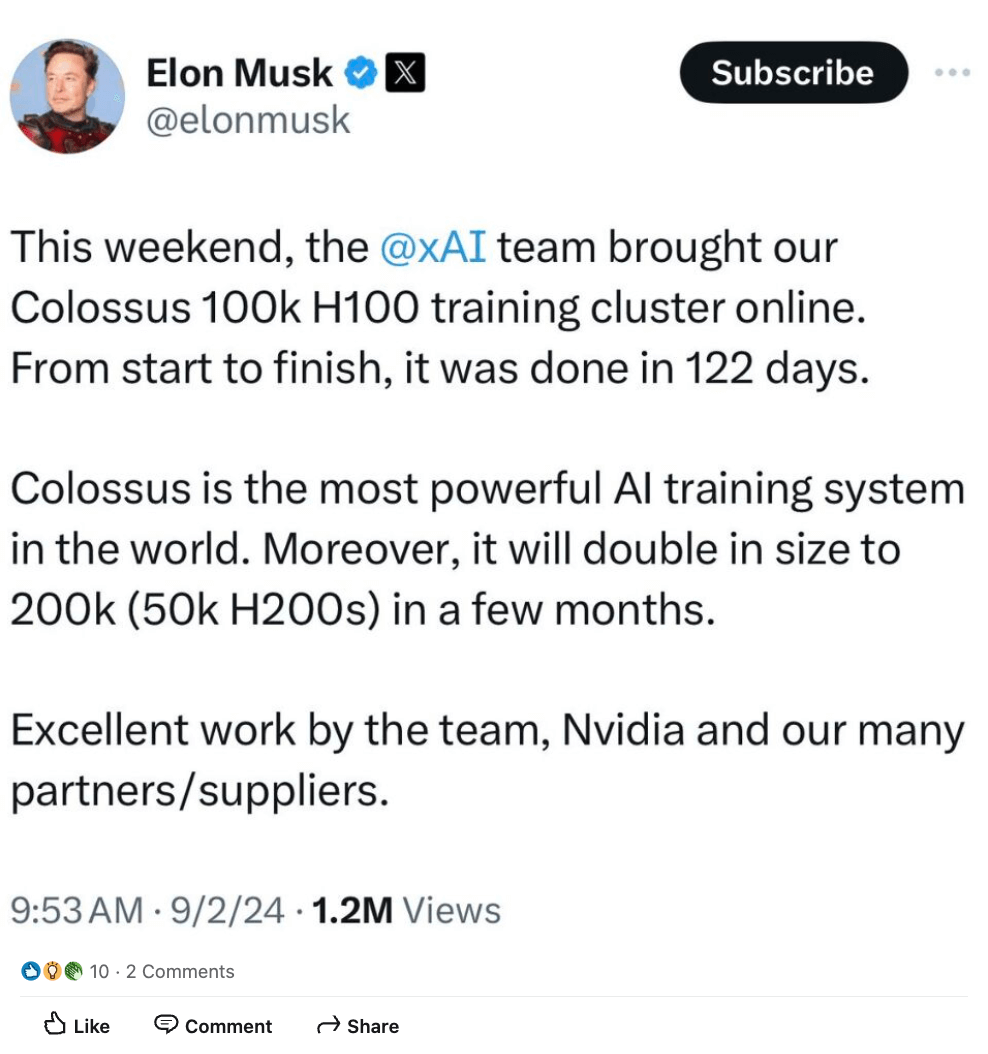
While availability of the H100 has improved throughout 2024, interest in both H100 and H200 remain high. To give you an understanding of the scale, Elon Musk recently announced the activation of a 100k H100 training cluster for xAI, with plans to add an additional 50k H200s to the system within months.
Bottom line on the H200 vs H100
As we await the full roll-out of next-generation systems like the GB200, both the H100 and H200 are going to challenge the frontiers of AI development for years to come. As AI models continue to grow in size, we’ll see an increased need for computational speed and efficiency. The H200 will be a great option when it is available. Until then, the H100 remains your best option. Spin up an instance on the DataCrunch Cloud Platform today!
